How to treat and prevent leg muscle cramps
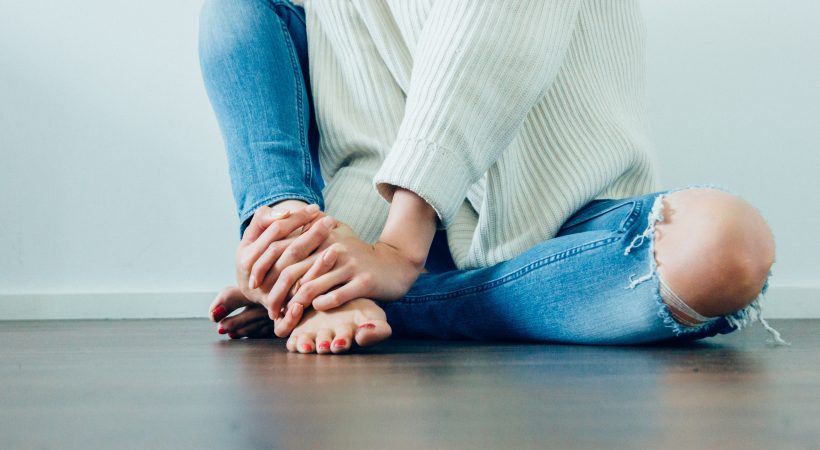

Muscle cramps are painful, visible contractions of a muscle or part of a muscle. Many people experience muscle cramps in the calf. In most cases, the cramp can last for a few seconds to a few minutes.
Who is at risk
Leg muscle cramps can affect anyone, but those who are more at risk include:
People with overweight or obesity
Athletes
People taking certain medications
Older adults, particularly those aged 65 and over
Pregnant women
Causes
Muscle cramp occurs when the surrounding neurons repetitively stimulate it. Leg muscle cramps are a common occurrence.
According to some researchers, the exact causes of leg muscle cramps are largely unknown, but some triggers can include:
Exercise
Pregnancy
The presence of nocturnal leg cramps
Dehydration
Certain medications
Sometimes, leg muscle cramps can be a symptom of an underlying medical condition. These might include:
A neurological condition, such as motor neuron disease
An infection, such as tetanus liver disease
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Ingesting toxins such as lead or mercury can also cause muscle cramps.
If a person believes that he has ingested one or both of these toxins, they should seek emergency medical attention.
To provide some relief, a person can:
Stretch the muscle
Get a deep tissue massage
Apply a hot or cold compress to the affected area
In pregnant women, magnesium and multivitamins may help.
Prevention
If a person suspects that their cramps are due to serious medical concerns such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or the ingestion of toxins, they should seek emergency medical attention.
However, for benign cramps, staying hydrated and maintaining a healthful diet may help in preventing leg muscle cramps.
Before exercising, a person should be sure to stretch the muscles and drink plenty of water.
Helpful foods
Many people believe that taking magnesium supplements can help prevent muscle cramps. In fact, some vitamin and mineral supplement companies actually market magnesium supplements for muscle cramp prevention.
Foods that are high in magnesium include:
Almonds
Spinach
Cashew nuts
Peanuts
Soy-milk
Black beans
Edamame
Baked potatoes with skin
Cooked brown rice
Plain, low fat yogurt
However, it is important to note that studies have not yet confirmed that magnesium is effective for the prevention of leg muscle cramps.
Is it serious?
When leg muscle cramps occur as a result of exercise or standing for too long, the body needs rest. In these cases, the symptoms should resolve on their own.
When leg muscle cramps become persistent, however, a person may also notice that they are not sleeping well, or that they feel limited in their daily activities. Although not serious, these persistent symptoms can impact a person’s quality of life.
If a person experiences muscle cramps along with other symptoms, such as swelling or skin discoloration, they should seek emergency medical help, as it may be a symptom of DVT.
Cramps that occur in young, healthy people and resolve spontaneously do not usually require medical attention.
If leg muscle cramps become recurrent or start to affect a person’s quality of life and daily activities, they should make an appointment with their doctor.
However, in most situations, leg muscle cramps are not serious and will go away on their own. Information courtesy: Medical News Today